During your experience as a SQL Server Database Administrator, you may work with applications that store data as comma-separated values in a single column. To deal with this de-normalized data, you may need to normalize it to work with each single value separately in your SQL Server code or provide this normalized data to another data source. We used to write such user defined functions that takes a string, loops through it, searching for the delimiter and retrieve a table with these separated values. What is hidden for us in SQL Server 2016 to achieve this task more efficiently?
Solution
SQL Server 2016 introduced a new built-in table-valued function, STRING_SPLIT that splits the provided input string by a specified separation character and returns the output separated values in the form of table, with a row for each delimited value between each separator character.
STRING_SPLIT function takes two parameters:
STRING_SPLIT ( string , separator )
The string is an expression of characters with char, nchar, varchar or nvarchar data types. The separator is a single character that will be used to separate the concatenated input string, with char, nchar, varchar or nvarchar data types.
STRING_SPLIT returns a single column table. The name of the returned column is value. The default data type of the value column is varchar. If the input string data type is nvarchar or nchar, the value column data type will be nvarchar. The length of the value column will be the same as the length of the string that will be split.
Database Compatibility Level Error for STRING_SPLIT Function
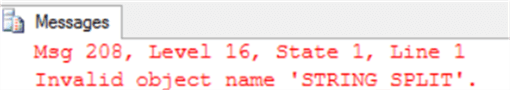
Before using the STRING_SPLIT function, you should make sure that the database compatibility level is 130. In my case, my local SQL Server instance was upgraded from SQL Server 2014 version to SQL Server 2016 version. So that, if I try to run the below simple straight-forward call for the STRING_SPLIT function on my database, providing it with a string to be separated and a comma as a separator:
SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT('John,Jeremy,Jack',',') GO
The query will fail showing that this function is not available. This is expected in my case, as the database compatibility level will not be changed to the new version automatically when we upgrade the current SQL Server instance:
In order to be able to use the STRING_SPLIT function, we should change the compatibility level of the database to 130 using the below ALTER DATABASE T-SQL statement:
USE [master] GO ALTER DATABASE [MSSQLTipsDemo] SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 130 GO
Now the compatibility level of the database is modified to 130 to use the STRING_SPLIT function. Running the same SELECT statement again:
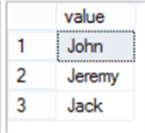
SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT('John,Jeremy,Jack',',')
You will see clearly that the STRING_SPLIT loops through the provided string, searches for the comma inside that string and returns a row for each separated value as shown below:
WHERE Clause with the STRING_SPLIT Function
The result that is returned from the STRING_SPLIT function can be filtered using the WHERE clause and ordered using the ORDER BY clause. The previous result can be sorted using the T-SQL below statement:
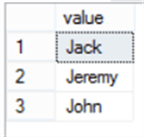
SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT('John,Jeremy,Jack',',') ORDER BY value asc
The sorted result will be like:
Pass Parameters into the STRING_SPLIT Function
STRING_SPLIT parameters can also be passed as variables with different values. In the below script, two variables are declared; one to store the string to be delimited and the second one for the separator value:
DECLARE @String VARCHAR(50) = 'John,Jeremy,Jack', @Delimiter CHAR(1) =',' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
Executing the previous query, the same result will be returned as follows:
Separator Character for STRING_SPLIT Function
As mentioned previously, the separator is a single character that is used by the function as a separation criteria. If you try to separate the input string using two characters separator:
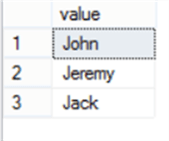
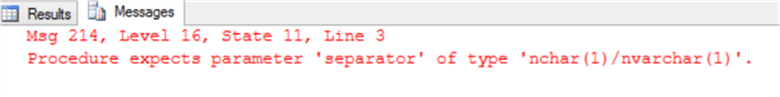
DECLARE @String VARCHAR(50) = 'John*$Jeremy*$Jack', @Delimiter CHAR(2) ='*$' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
The function will fail, showing that it should be always a single character of the CHAR(1), VARCHAR(1), NVARCHAR(1) and NCHAR(1) datatypes:
Defining the separator as a single character:
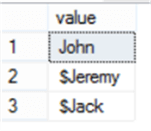
DECLARE @String VARCHAR(50) = 'John*$Jeremy*$Jack', @Delimiter CHAR(1) ='*' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
The result will be like:
Unicode Separator for STRING_SPLIT Function
Both the string that will be delimited and the separator can take Unicode values by defining the string as NVARCHAR and the delimiter as NCHAR. In the following example, a string written in Arabic language will be separated by an Arabic character:
DECLARE @String NVARCHAR(50) = N'ÃÍãÏ æ ãÍãÏ æ ãÄíÏ', @Delimiter NCHAR(1) =N'æ' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
The separated Arabic values will be like:

NULL Separator for STRING_SPLIT Function
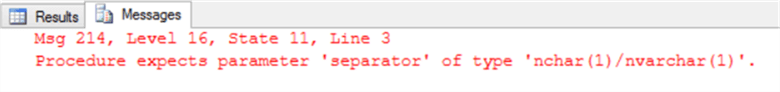
The separator also cannot be passed as NULL, if you define the delimiter value as NULL:
DECLARE @String VARCHAR(50) = 'John,Jeremy,Jack', @Delimiter CHAR(1) = NULL SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
The function will fail again showing the same previous error:
The input string is another case. If you try to pass the string to be delimited as NULL:
DECLARE @String VARCHAR(50) = NULL, @Delimiter CHAR(1) =',' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
The function will not fail, but an empty table will be returned from the function as below:

If no value is specified after the delimiter as in this script:
DECLARE @String VARCHAR(50) = 'John,Jeremy,', @Delimiter CHAR(1) =',' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter)
This unspecified value will be treated as an empty string with empty value returned as a separate row and not NULL value, as shown in the result below:
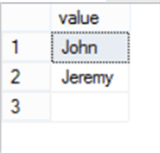
Clean De-Normalized Data with the STRING_SPLIT Function
SQL Server Cursor with STRING_SPLIT Function
The STRING_SPLIT function will be useful also in specific cases, in which you need to clean de-normalized data in a specific table and insert it into another table to use it there. In order to use the STRING_SPLIT function to parse the data in the table row by row, the first method appears in our minds to do that is using the cursors. The below script defines a cursor that reads the ProductID and the Name from the Product table, and separates the value of each name using the space delimiter and insert the generated result into a temp table defined at the beginning of the script:
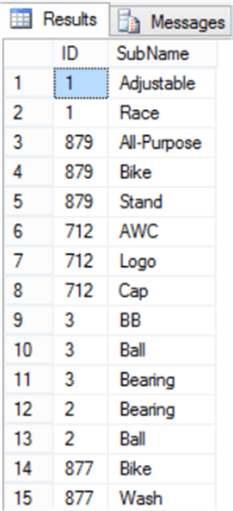
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO CREATE TABLE #TempSubProduct(ID int , SubName varchar(50)) DECLARE @PID INT DECLARE @Name VARCHAR(100) DECLARE Split_Product CURSOR LOCAL FAST_FORWARD FOR SELECT ProductID , Name FROM Production.Product OPEN Split_Product FETCH NEXT FROM Split_Product INTO @PID, @Name WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN INSERT INTO #TempSubProduct SELECT @PID, SPL.value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@Name,' ') AS SPL FETCH NEXT FROM Split_Product INTO @PID, @Name END SELECT * FROM #TempSubProduct DROP TABLE #TempSubProduct
A sample of the generated result in our case will be like:
SQL Server CROSS APPLY with STRING_SPLIT Function
The same previous process can be performed by replacing the cursor by the CROSS APPLY method as follows:
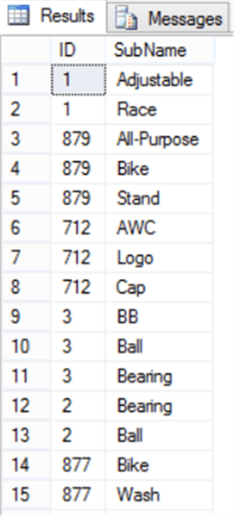
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO CREATE TABLE #TempSubProduct(ID int , SubName varchar(50)) INSERT INTO #TempSubProduct (ID, SubName) SELECT ProductID, SPL.value FROM Production.Product AS PP CROSS APPLY STRING_SPLIT(PP.Name,' ') AS SPL; SELECT * FROM #TempSubProduct DROP TABLE #TempSubProduct
With the same returned result that will be like:
SQL Server JOIN with STRING_SPLIT Function
Another use for the STRING_SPLIT function is to find specific rows in a table. What you need to do is to pass a specific column values to the STRING_SPLIT function as the string to be separated and join the main table with the STRING_SPLIT function result. In the below script, we pass a list of comma-separated IDs from the Product table and join it with the Product table to retrieve the name of products with these IDs from the main table:
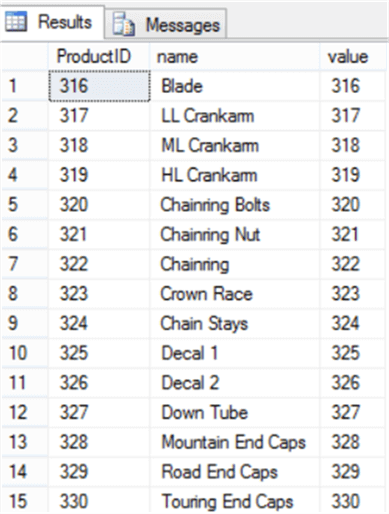
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO SELECT PP.ProductID, PP.name, SPL.value FROM Production.Product PP JOIN STRING_SPLIT('316,317,318,319,320,321,322,323,324,325,326,327,328,329,330', ',') AS SPL ON SPL.value = PP.ProductID
And the results will look like:
User Defined STRING_SPLIT Function Example
To encourage ourselves to use the STRING_SPLIT built-in function to replace the legacy functions we used to split string values, we will create a user-defined split function. Here is one example:
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO CREATE FUNCTION [dbo].[SplitString] ( @String NVARCHAR(4000), @Delimiter NCHAR(1) ) RETURNS TABLE AS RETURN ( WITH Split(stpos,endpos) AS( SELECT 0 AS stpos, CHARINDEX(@Delimiter,@String) AS endpos UNION ALL SELECT endpos+1, CHARINDEX(@Delimiter,@String,endpos+1) FROM Split WHERE endpos > 0 ) SELECT 'Id' = ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY (SELECT 1)), 'Value' = SUBSTRING(@String,stpos,COALESCE(NULLIF(endpos,0),LEN(@String)+1)-stpos) FROM Split )
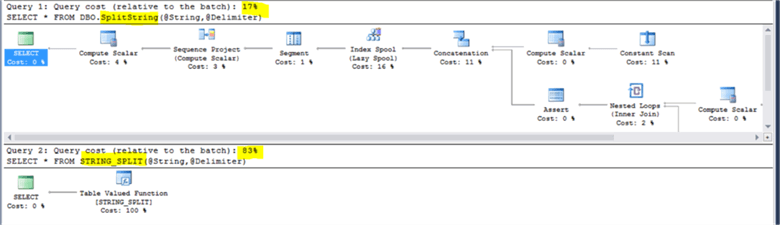
Once the split function is created successfully, let us try to separate a specific string twice, the first time using the created user-defined split function and the second time using the built-in STRING_SPLIT function, enabling the time statistics and the actual execution plan to have a reasonable comparison:
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO SET STATISTICS TIME ON DECLARE @String VARCHAR(100) = 'John,Jeremy,Jack,Ali,Mohammed,Ahmad,Zaid,Kenan,Kinda,Saed', @Delimiter CHAR(1) =',' SELECT * FROM DBO.SplitString(@String,@Delimiter) GO DECLARE @String VARCHAR(100) = 'John,Jeremy,Jack,Ali,Mohammed,Ahmad,Zaid,Kenan,Kinda,Saed', @Delimiter CHAR(1) =',' SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT(@String,@Delimiter) GO SET STATISTICS TIME OFF
Both functions returned the same result as follows:
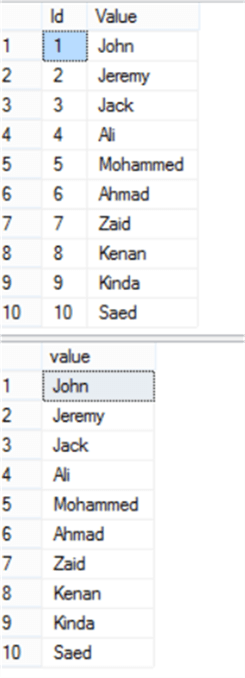
But the important question is, how much it takes each function to return the result? From the time statistics, the user-defined split function took 29 ms to separate the defined string, where it took the STRING_SPLIT built-in function 0 ms to separate the same string.

The performance difference is also clear by comparing the execution plans generated by each run. The weight of the user defined split function execution plan is about 5 times the weight of the STRING_SPLIT execution plan as shown below: