Traditional monolithic style application architecture coupled all their functionality tightly into one service. This caused high difficulty to deploy new features as it will take long downtimes which resulted in fewer opportunities to make updates to the application. Scaling such applications are expensive because we have to scale the whole application even though only a particular service gets much traffic.
The introduction of the cloud has brought a drastic change in the way we design, architect and deploy our applications. Helped in faster deployments, improving availability, ability to scale on demand and reduced the time to market. So here comes in the Microservices-based application, which is an architecture in which the goal is to create smaller isolated services that can deploy and scale independently of each other improving the agility.
Microservices Principles
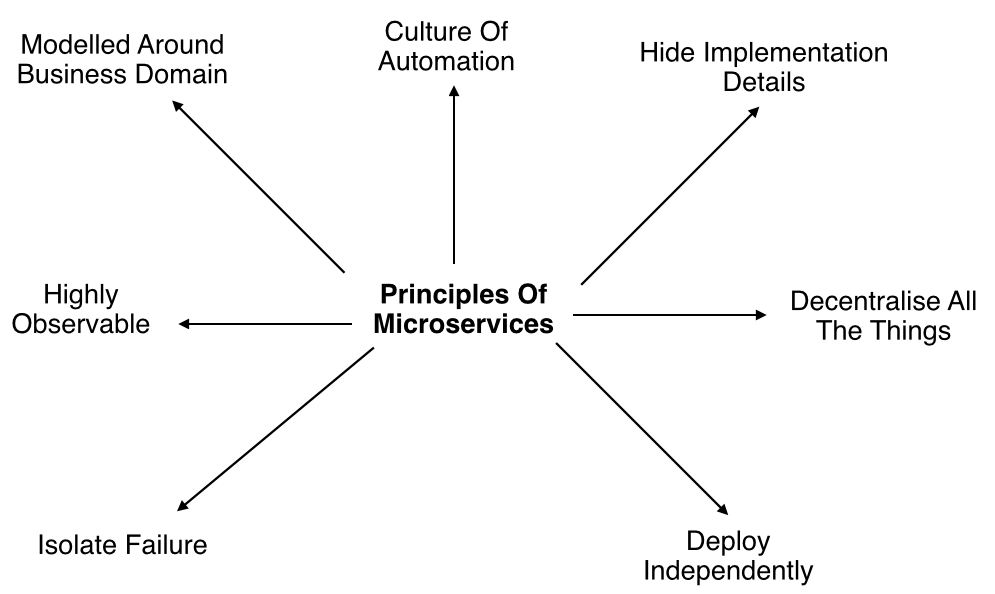
- Modelled around business domain : Microservices architecture lets us separate system capability into different domains. Each domain will focus on one thing and its associated logic and can easily migrate independently to the next version, and also scale independently according to requirement.
- Culture of Automation : As we are building, testing, deploying and monitoring each service separately and there is an increase in the number of deployment units compared to monolithic architecture we should follow the culture of automation by designing it for continues integration and continuous delivery.
- Hide implementation details : Microservices should be architected in such a way that it won’t expose the internal details; neither technical implementation nor the business rules that drive it. This will reduce the coupling and helps to do changes and improvement without affecting the overall architecture.
- Decentralization : In traditional monolithic implementations, the software is designed to use a single database with different tables where microservices is designed in such a way to manage its own database.
- Deploy Independently : To enjoy the complete benefits of the architecture, microservices should be independently deployable. If you are failing to do so, check for any coupling in the application and solve it.
- Failure Isolation : The impact of a failure is less in microservice architecture compares to monolithic type as it will only affect that particular services and its associated while other services can keep running. The associated services should handle such scenarios when dependent is unresponsive or slow.
- Highly Observable : The services should collect as much information to analyze what is happening within each of them like log events and stats.
Monolithic vs. SOA vs. Microservices
Monolithic architectures are the simplest form of architecture as it is having only one application layer that bundles together all the software components, and is hosted and delivered together. This type has been widely used by many small and mid-sized companies. The main challenge in this system is during scaling up as we need to duplicate the whole system including all the features of other machines which increases the cost. Also, the failure of one feature will affect the whole system making it unreliable.
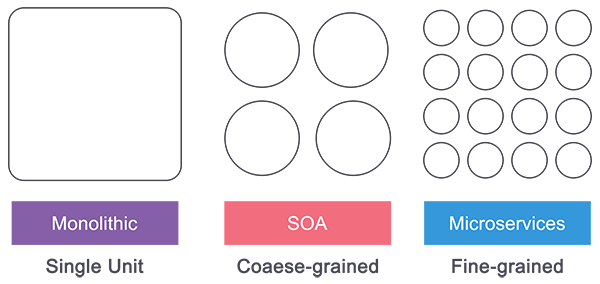
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) follows a coarse-grained structure where the features of an application are broken down into smaller components as services comprised of some tasks. This type of architecture allowed us to horizontally scale each service, and also more flexibility and performance at the cost of increasing the complexity of the architecture compared to the monolithic. Each service can be written in different languages and the communication between them can be done with the help of a middleware
Microservices has technically evolved out of SOA where those features are further broken down into tasks level services making it fine-grained architecture. While Service Oriented Architecture followed a centrally governed architecture where each component is controlled by a central middleware, in microservices it’s a decentralized governing system where components talk directly to each other and can be written in different programming languages and communicate without the help of any broker and are done with the help of REST API.
Microservices Architecture
An architectural style that structures an application as a collection of small self-contained processes, modelled around a business capability. They don’t share the data structure and will be communicating through APIs. While in a monolithic application all the components being in a single module, in microservices we can see all the components are divided into a separate module and communication happens with each other with the help of APIs. In Microservices Architecture the data is federated where each microservices is responsible for its own data model and data.
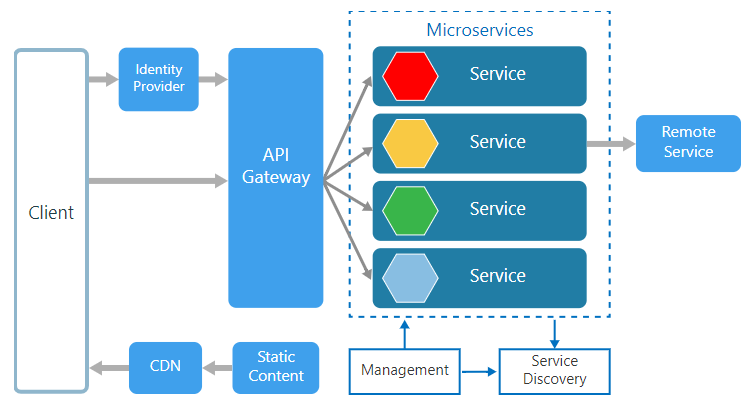
Source:https://docs.microsoft.com
Being small in size, independent and loosely coupled each service can be developed and deployed independently by a small team as each service is having its own code base. Data and state persistence should be taken with each service as it lacks a separate data layer to handle it. The services only communicate with well-defined APIs hiding each service’s internal implementation from each other. Each service can use different technology stack, language, libraries or frameworks.
- Management : The Management take care of placement of services on nodes, checking for failures, rebalancing services across nodes in case of any failures.
- Service Discovery : Maintains a list of services and the nodes where each service are located, and also enables the service to look up to find the endpoint for a particular service.
- API Gateway : The entry point for clients where all the calls from the client will be taken, analyze it and forward to appropriate services. In case some calls needed from multiple services API Gateway will aggregate and will return the aggregated result.
Companies using Microservices
There are many companies using Microservices for their products and services and here is a list of few who shared their experiences.
- Comcast Cable
- Uber
- Netflix
- Amazon
- eBay
- Sound Cloud
- Karma
- Microsoft
- Groupon
- Hailo
- Gilt
- Zalando
- Lending Club
- AutoScout24
Advantages of Microservices
- Services can be written in different programming language and can be accessed by using any framework.
- Independently develop, deploy, redeploy, version and scale component services in seconds without compromising the integrity of an application
- Better fault isolation keeps other services to work even though on got failed.
- Zero downtime upgrades.
- Services can be of from different servers or even different datacenters.
- Interaction with other services in a well-defined protocol
- Monitor, capture, and report health diagnostics
- Reliable and self-healing
- Supports continuous integration and delivery
- Easy to transfer knowledge to the new team member
- Easy to integrate with third parties
Disadvantages of Microservices
- The additional complexity for implementation of an inter-process communication mechanism between services.
- Writing automated tests involving multiple services is challenging and It can be difficult to create consistent testing environments.
- Requires high level of automation to manage multiple instances of different types of services in production.
- Everyone has to manage eventual consistency as maintaining string consistency becomes extremely difficult.
- Managing multiple databases and their transactions are difficult.
- Inter-process calls are slow.
- Debugging will become difficult.
- Complexity in DevOps.
- Production monitoring cost is higher.
- Formal documentation overhead.
- Lack of governance.
No comments:
Post a Comment