In this article I will explain with an example, how to implement a simple login form using Forms Authentication which validates user login from database and also redirects user to Login page if the user is not Authenticated (logged in) and tries to access a page that requires authentication in ASP.Net MVC Razor.
The Login page URL will be set in the authentication section of the Web.Config file and the User will be redirected back to Login page if not logged in using the Authorize Data Annotation attribute in ASP.Net MVC Razor.
Configuring Bundles and enabling Client Side Validation
The User Login Form validation will be performed on Client Side using Model Data Annotations and jQuery.
Please refer the following article for complete information on how to configure Bundles and enable Client Side validation in ASP.Net MVC project.
Using Bundles (ScriptBundle) in ASP.Net MVC Razor
Database
I am making use of the same database table Users which was used in the article Simple User Registration Form with Entity Framework Database in ASP.Net MVC.
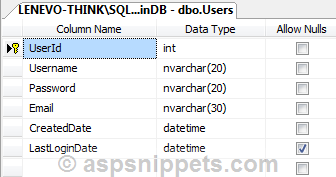
Stored Procedure to Validate the User Credentials
The following stored procedure is used to validate the user credentials, this stored procedure first checks whether the username and password are correct else returns -1.
If the username and password are correct but the user has not been activated then the code returned is -2.
If the username and password are correct and the user account has been activated then UserId of the user is returned by the stored procedure.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[Validate_User]
@Username NVARCHAR(20),
@Password NVARCHAR(20)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @UserId INT, @LastLoginDate DATETIME
SELECT @UserId = UserId, @LastLoginDate = LastLoginDate
FROM Users WHERE Username = @Username AND [Password] = @Password
IF @UserId IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT UserId FROM UserActivation WHERE UserId = @UserId)
BEGIN
UPDATE Users
SET LastLoginDate = GETDATE()
WHERE UserId = @UserId
SELECT @UserId [UserId] -- User Valid
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT -2 -- User not activated.
END
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT -1 -- User invalid.
END
END
Adding new Stored Procedure to the Entity Framework Data Model
The Entity Framework has been already configured in the User Registration article and hence we will continue with further step i.e. adding the new Stored Procedure (discussed earlier) to the existing Entity Framework Data Model.
To do so, open the User Data Model and then Right click on the User Table and click on the Update Model from Database option from the Context menu.
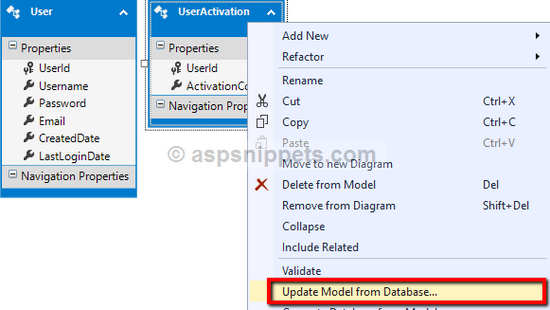
The above action will open the Update Wizard dialog window, where you will need to select the newly added Stored Procedure and click Finish button.
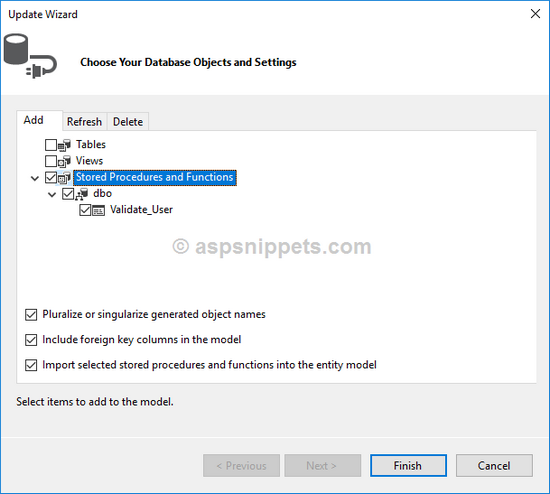
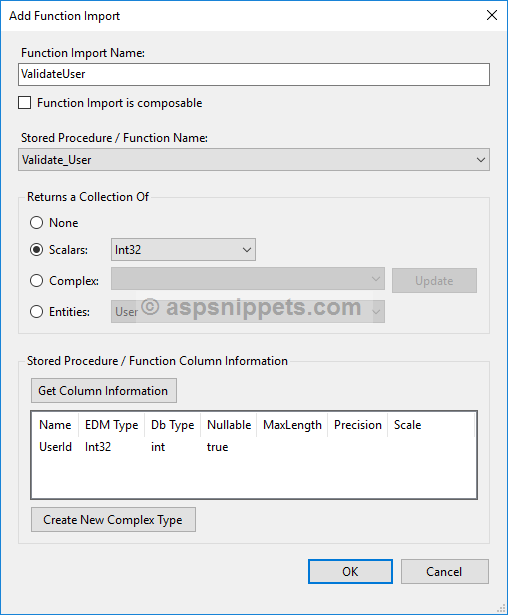
Once the Stored Procedure is added you will again need to Right click on the User Table and click on Add New option and then Function Import option from the Context menu.
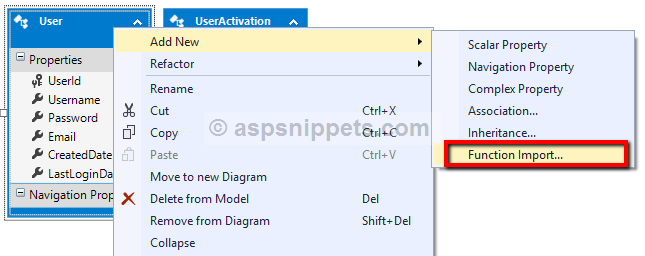
The above action will open the Add Function Import Dialog window. Here you will need to
1. Function Import Name: Specify the name of the method which will be used to execute the Stored Procedure.
2. Stored Procedure / Function Name: Select the Stored Procedure / Function to be imported.
3. Returns a Collection Of: The Stored Procedure used in this article returns a Scalar value and hence the same is selected.
Finally once all the above is done, simply click the OK button.
Model
The Model class User.cs remains the same as the User Registration article except one change i.e. a new property RememberMe has been added.
namespace User_Login_MVC
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
public partial class User
{
public int UserId { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Required.")]
public string Username { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Required.")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Required.")]
[Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "Passwords do not match.")]
public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Required.")]
[EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "Invalid email address.")]
public string Email { get; set; }
public System.DateTime CreatedDate { get; set; }
public Nullable<System.DateTime> LastLoginDate { get; set; }
public bool RememberMe { get; set; }
}
}
Namespaces
You will need to import the following namespace.
using System.Web.Security;
Controller
The Controller consists of four Action methods.
Action method for handling GET operation for Login
Inside this Action method, simply the View is returned. This Action method is decorated with AllowAnonymous Data Annotation which signifies Form Based authentication that this method can be accessed without authentication.
Action method for handling GET operation for Profile
Inside this Action method, simply the View is returned. This Action method is decorated with Authorize Data Annotation which signifies Form Based authentication that this method requires authentication to be accessed.
Action method for handling POST operation for Login
Inside this Action method, the ValidateUser method is called which executes the Stored Procedure that validates the User’s credentials.
The status returned from the Stored Procedure is captured and if the value is not -1 (Username or password incorrect) or -2 (Account not activated) then the user is redirected to the Profile View after setting the Forms Authentication Cookie.
For the status -1 and -2, the message is displayed to the user using ViewBag object.
Action method for handling POST operation for Logout
Inside this Action method, the Signout method of Forms Authentication is called which clears the Forms Authentication Cookie and the user is redirected to the Index View.
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[AllowAnonymous]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize]
public ActionResult Profile()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
[AllowAnonymous]
public ActionResult Index(User user)
{
UsersEntities usersEntities = new UsersEntities();
int? userId = usersEntities.ValidateUser(user.Username, user.Password).FirstOrDefault();
string message = string.Empty;
switch (userId.Value)
{
case -1:
message = "Username and/or password is incorrect.";
break;
case -2:
message = "Account has not been activated.";
break;
default:
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(user.Username, user.RememberMe);
return RedirectToAction("Profile");
}
ViewBag.Message = message;
return View(user);
}
[HttpPost]
[Authorize]
public ActionResult Logout()
{
FormsAuthentication.SignOut();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
Views
Index
Inside the View, in the very first line the User Model class is declared as Model for the View.
The View consists of an HTML Form which has been created using the Html.BeginForm method with the following parameters.
ActionName – Name of the Action. In this case the name is Index.
ControllerName – Name of the Controller. In this case the name is Home.
FormMethod – It specifies the Form Method i.e. GET or POST. In this case it will be set to POST.
Inside the View, the following four HTML Helper functions are used:-
1. Html.TextBoxFor – Creating a TextBox for the Model property.
2. Html.PasswordFor – Creating a Password TextBox for the Model property.
3. Html.ValidationMessageFor – Displaying the Validation message for the property.
4. Html.CheckBoxFor – Creating a CheckBox for the Model property.
There is also Submit button which when clicked, the Form gets submitted.
The jQuery and the jQuery Validation script bundles are rendered at the end of the Model using the Scripts.Render function.
ViewBag’s Message object is checked for NULL and if it is not NULL then the string message is displayed using JavaScript Alert Message Box.
@model User_Login_MVC.User
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width"/>
<title>Index</title>
<style type="text/css">
body {
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 10pt;
}
table {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
table th {
background-color: #F7F7F7;
color: #333;
font-weight: bold;
}
table th, table td {
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.error {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
@using (Html.BeginForm("Index", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{
<table border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<th colspan="3">
Login
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Username
</td>
<td>
@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.Username)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.Username, "", new { @class = "error" })
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Password
</td>
<td>
@Html.PasswordFor(m => m.Password)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.Password, "", new { @class = "error" })
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Remember Me
</td>
<td>
@Html.CheckBoxFor(m => m.RememberMe)
</td>
<td>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="Submit"/>
</td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
}
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jquery")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
@if (@ViewBag.Message != null)
{
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
alert("@ViewBag.Message")
});
</script>
}
</body>
</html>
Profile
The Profile View displays the name of the Current Logged in User and it also consists of an HTML Form with an HTML Anchor link for Logout functionality.
When the Logout link is clicked, the Form gets submitted and the Logout Action method gets called.
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width"/>
<title>Profile</title>
<style type="text/css">
body {
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 10pt;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
Welcome
<b>@HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name</b>
<br/>
<br/>
@using (Html.BeginForm("Logout", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{
<a href="javascript:;" onclick="document.forms[0].submit();">Logout</a>
}
</div>
</body>
</html>
Web.Config Configuration
You will need to add the following configuration in the Web.Config file in the <system.web> section.
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms defaultUrl="/Home/Profile" loginUrl="/Home/Index" slidingExpiration="true" timeout="2880"></forms>
</authentication>
No comments:
Post a Comment