A blockchain is a constantly growing ledger which keeps a permanent record of all the transactions that have taken place in a secure, chronological, and immutable way.
Let's breakdown the definition,
- Ledger: It is a file that is constantly growing.
- Permanent: It means once the transaction goes inside a blockchain, you can put up it permanently in the ledger.
- Secure: Blockchain placed information in a secure way. It uses very advanced cryptography to make sure that the information is locked inside the blockchain.
- Chronological: Chronological means every transaction happens after the previous one.
- Immutable: It means as you build all the transaction onto the blockchain, this ledger can never be changed.
A blockchain is a chain of blocks which contain information. Each block records all of the recent transactions, and once completed goes into the blockchain as a permanent database. Each time a block gets completed, a new block is generated.
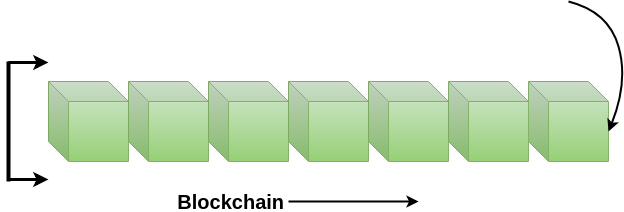
Note: A blockchain can be used for the secure transfer of money, property, contracts, etc. without requiring a third-party intermediary like bank or government. Blockchain is a software protocol, but it could not be run without the Internet (like SMTP used in email).
Who uses the blockchain?
Blockchain technology can be integrated into multiple areas. The primary use of blockchains is as a distributed ledger for cryptocurrencies. It shows great promise across a wide range of business applications like Banking, Finance, Government, Healthcare, Insurance, Media and Entertainment, Retail, etc.
Need of Blockchain
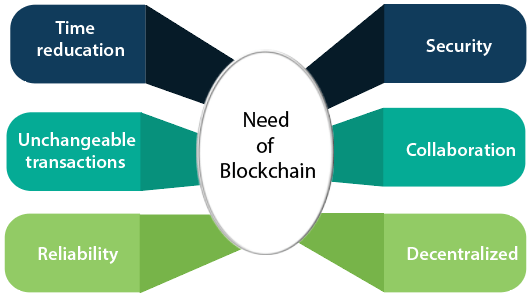
Blockchain technology has become popular because of the following.
- Time reduction: In the financial industry, blockchain can allow the quicker settlement of trades. It does not take a lengthy process for verification, settlement, and clearance. It is because of a single version of agreed-upon data available between all stakeholders.
- Unchangeable transactions: Blockchain register transactions in a chronological order which certifies the unalterability of all operations, means when a new block is added to the chain of ledgers, it cannot be removed or modified.
- Reliability: Blockchain certifies and verifies the identities of each interested parties. This removes double records, reducing rates and accelerates transactions.
- Security: Blockchain uses very advanced cryptography to make sure that the information is locked inside the blockchain. It uses Distributed Ledger Technology where each party holds a copy of the original chain, so the system remains operative, even the large number of other nodes fall.
- Collaboration: It allows each party to transact directly with each other without requiring a third-party intermediary.
- Decentralized: It is decentralized because there is no central authority supervising anything. There are standards rules on how every node exchanges the blockchain information. This method ensures that all transactions are validated, and all valid transactions are added one by one.
No comments:
Post a Comment